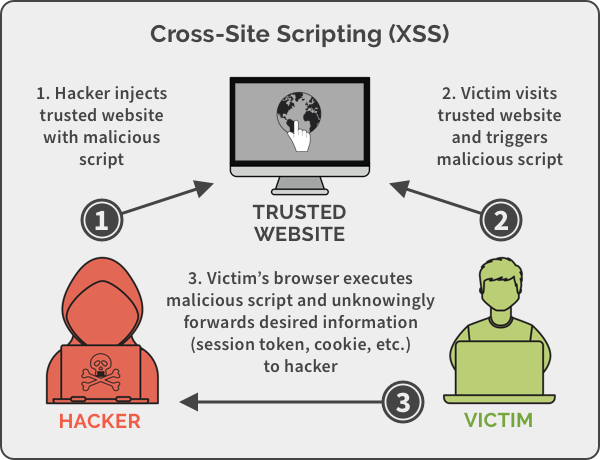
Cross-Site Scripting attack XSS
you will find in this link book talk about web attack
click here


click here
"One of the major attack victors of all time"
what is XSS attack ?
XSS attacks enable attackers to inject client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users
Major types of XSS:
XSS vulnerabilities come in various forms and may be divided into three varieties: reflected, stored, and DOM-based. Although these have several features in common, they also have important differences in how they can be identified and exploited. We will examine each variety of XSS in turn
Reflected XSS:
it is those where the injected script is reflected off
the web server such as in an error message, search result , or any response that include inputs sent to the server as
part of the request, Reflected attacks are delivered to victims via another route , this type activated when victim or our visitor is clicking on link or just browsing to a malicious site the
injected code travels to the vulnerable web site, which reflects the
attack back to the user’s browser. The browser then executes the code
because it came from a “trusted” server
- Exploit URL:
http://www.nikebiz.com/search/?q=<script>alert('XSS')</script>&x=0&y=0
- HTML returned to victim:
<div id="pageTitleTxt"> <h2><span class="highlight">Search Results</span><br/> Search:"<script>alert('XSS')</script>"</h2>
stored xss :
Stored attacks are those where the injected script is permanently stored on the target servers, such as in a database, in a message forum, log in comment field, etc. The victim then retrieves the malicious script from the server when it requests the stored information
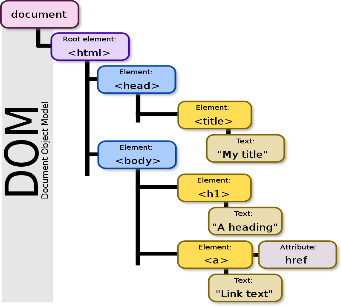
DOM-based:
first what is DOM:
Both reflected and stored XSS vulnerabilities involve a specific pattern of behavior, in which the application takes user-controllable data and displays this back tousers in an unsafe way. A third category of XSS vulnerabilities does not share this characteristic
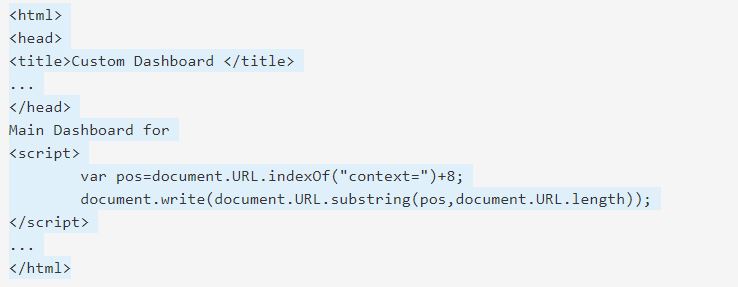
- The attacker embeds a malicious script in the URL:
http://www.example.com/userdashboard.html#context<script>SomeFunction(somevariable)</script>.
- The victim’s browser sends HTTP request and receives the static HTML page.
- The browser starts building the DOM of the page
- The browser parses the HTML page, reaches the script, and runs it, extracting the malicious content from the document.URL property.
- The browser finds the JavaScript code in the HTML body and executes it.
Protect your WA from injection:
➢ Validate Input
➢ Letters in a number field ?
➢ 10 digits for 4 digit year field?
➢ Careful with < > " ' and =
➢ Whitelist (e.g. /[a-zA-Z0-9]{0,20}/)
What can you do with JavaScript?
➢ Pop-up alerts and prompts
➢ Access/Modify DOM
➢ Access cookies/session tokens
➢ Detect installed programs
➢ Detect browser history
➢ Capture keystrokes (and other trojan functionality)
➢ Port scan the local network
thanks for read this articles
give us like in facebook link

Comments
Post a Comment